
Archives
-

Real-Time Vehicle License Plate Detection and Recognition Using YOLOv5
Vol. 2 No. 03 (2025)ABSTRACT
The project titled "Vehicle Number Plate Detection and Extraction using YOLO V5" focuses on developing an efficient system for automating the identification and extraction of license plates from images or video streams. The implementation utilizes the YOLO V5 (You Only Look Once) object detection model, known for its real-time processing capabilities.
The project begins with the collection and preparation of a diverse dataset containing images of vehicles, ensuring adequate representation of various license plate types, sizes, and environmental conditions. This dataset is then used to train the YOLO V5 model, fine-tuning its parameters for accurate and robust license plate detection.
Upon successful training, the model is deployed to analyze new input data. During the inference phase, the YOLO V5 model identifies the regions of interest corresponding to license plates within the images or video frames. Subsequently, a mechanism is implemented to extract the license plate information, including alphanumeric characters.
KEYWORDS
- YOLOv5
- Vehicle number plate
- Detection
- Extraction
- Computer vision
- Deep learning
- Image processing
- Object detection
- ANPR (Automatic Number Plate Recognition)
-

The CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION TRAKER AND SUSPECT DETECTION
Vol. 1 No. 1 (2024)Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive system designed to assist law enforcement agencies in tracking criminal activities and detecting suspects efficiently using the MERN stack. The developed system integrates MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js to handle large volumes of data with high responsiveness. This paper details the system architecture, implementation, testing methodologies, and the tangible benefits observed during initial deployments.
Index Terms
Criminal Investigation, Suspect Detection, MERN Stack, Real-Time Systems, Law Enforcement Technologies.
-

Enhancing Climate Resilience through Machine Learning-Driven Insights
Vol. 2 No. 06 (2025)Abstract
Climate change poses significant challenges to communities worldwide, necessitating innovative solutions to enhance resilience against its impacts. This project focuses on leveraging Machine Learning (ML) techniques to strengthen climate resilience. The project aims to develop and implement ML algorithms to analyze diverse datasets related to climate patterns, extreme weather events, and environmental conditions.
The primary objectives include identifying patterns and trends within the data, enabling the prediction of climate-related risks and the optimization of resource allocation. The project will explore the application of ML in various domains, such as agriculture, infrastructure planning, disaster preparedness, and resource management, to develop adaptive solutions for communities.
Through the integration of ML, the project seeks to contribute to more effective decision-making processes and the development of proactive strategies to address climate-related challenges. The continuous learning and refinement of ML models will enable the creation of sustainable and adaptive systems, enhancing the resilience of communities to the dynamic impacts of climate change.
This student project not only provides an opportunity to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios but also underscores the significance of technology in fostering climate resilience for a sustainable future.
Index terms
Climate change, Machine Learning (ML), Resilience, Predictive modeling, Climate patterns, Extreme weather events, Environmental conditions, Resource allocation, Agriculture, Infrastructure planning, Disaster preparedness, Resource management, Decision-making processes, Adaptive solutions, Sustainable development, Proactive strategies, Community resilience, Data analysis, Model refinement, Real-world applications, Technology integration.
-

Predictive Modeling for Undergraduate Engineering Branch Allocation Leveraging Machine Learning to Optimize Admissions
Vol. 1 No. 04 (2024)The allocation of branches in the admission process of undergraduate engineering programs plays a crucial role in shaping the academic journey of students. With limited seats and diverse preferences among applicants, accurately predicting the branch allocation based on ranks becomes imperative for educational institutions. This project aims to develop a predictive model for branch allocation, leveraging historical data and machine learning techniques. By analyzing past admission trends, the project seeks to identify patterns and factors influencing branch preferences. Utilizing algorithms such as regression analysis and decision trees, the model will forecast the likelihood of a student being allocated to a specific branch based on their rank and other relevant parameters. The project will also explore the integration of student preferences and institutional requirements to enhance the accuracy of predictions. Ultimately, the proposed predictive model aims to assist admission committees in making informed decisions, optimizing branch allocation, and ensuring a fair and efficient admission process for aspiring engineering students.
-

Protecting Privacy in Community-Driven Sensing with Secure Aggregation
Vol. 2 No. 09 (2025)Mobile Crowd Sensing (MCS) leverages ubiquitous mobile devices to collect large-scale environmental, health, and urban data. While enabling powerful analytics, MCS faces significant privacy risks as user-contributed data often contains sensitive personal information such as location, health status, or behavior patterns. To ensure both utility and confidentiality, this work explores the integration of Differential Privacy (DP) and Secure Aggregation mechanisms for MCS platforms. We analyze privacy–utility trade-offs, present algorithms for local and global differential privacy, and design lightweight secure aggregation protocols suitable for resource-constrained mobile devices. The proposed framework ensures individual-level privacy, defends against inference attacks, and maintains high data utility for real-time analytics.
-

Innovative Dual Authentication Protocols for Cloud Data Storage and Sharing
Vol. 2 No. 01 (2025)Abstract
As cloud computing continues to revolutionize the way data is stored and shared, the security of sensitive information becomes a paramount concern. This BTech project delves into the design and implementation of a robust dual access control framework for cloud-based data storage and sharing. The proposed system aims to enhance the security posture of cloud environments by incorporating a two-tier authentication mechanism.
The dual access control system combines traditional authentication methods, such as usernames and passwords, with an additional layer of security, such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication. This two-pronged approach ensures that only authorized users can access and share data stored in the cloud, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
The project will involve the development of a prototype system, including the integration of authentication mechanisms and the establishment of secure data sharing protocols. Through rigorous testing and evaluation, the effectiveness of the dual access control system in safeguarding sensitive information will be assessed.
The outcomes of this project are expected to contribute to the advancement of cloud security practices, providing a valuable solution for organizations and individuals seeking enhanced protection for their data in cloud environments. The project aligns with the growing demand for innovative approaches to address the evolving challenges of securing information in the era of cloud computing.
Index Terms
Cloud computing, Data storage, Data sharing, Security, Dual access control, Authentication mechanisms, Two-tier authentication, Biometrics, Multi-factor authentication, Prototype development, Secure data sharing protocols, Testing and evaluation, Sensitive information, Data breaches, Cloud security practices, Innovative approaches, Organizational security, Individual security, Evolution of challenges.
-

Explainable Deep Learning Models for Autonomous Vehicle Decision-Making
Vol. 2 No. 11 (2025)Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely heavily on deep learning models for perception, planning, and control. While these models achieve high accuracy, they operate as black boxes, making their decision-making process opaque. Lack of interpretability in safety-critical environments limits trust, hinders debugging, and complicates regulatory approval. This paper proposes an explainable deep learning framework for AV decision-making by integrating state-of-the-art perception and control models with post-hoc explainability techniques, specifically SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations). Using simulated driving scenarios in the CARLA simulator and real-world datasets such as KITTI and nuScenes, the framework generates actionable explanations for vehicle actions, including lane changes, braking, and steering. Our results demonstrate that XAI techniques can highlight critical features influencing decisions, uncover model biases, and assist developers in improving AV reliability. The proposed framework enhances safety, transparency, and accountability, providing a practical path toward regulatory-compliant autonomous systems.
-

Integrated E-Commerce Platform for Agriculture: Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency and Farmer Empowerment
Vol. 2 No. 04 (2025)Abstract
The " Integrated E-Commerce Platform for Agriculture Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency and Farmer Empowerment" is a comprehensive technological solution designed to address the evolving needs of the agricultural sector. This project aims to create a user-friendly online platform that facilitates seamless transactions and collaboration between farmers, agribusinesses, and suppliers. The portal integrates various modules, including inventory management, order tracking, and payment processing, to streamline the agricultural supply chain.
The primary focus is on providing farmers with easy access to a diverse range of agricultural products and services, such as seeds, fertilizers, and equipment. The portal also serves as an information hub, offering valuable insights on best practices, market trends, and innovative farming techniques. By fostering a digital marketplace, the project aims to empower farmers, enhance their decision-making processes, and contribute to the overall efficiency and sustainability of the agricultural ecosystem.
Through this Integrated E-Commerce Portal, the project envisions creating a connected and collaborative environment for stakeholders in the agricultural value chain. This initiative not only supports farmers in making informed choices but also promotes transparency and efficiency in agricultural transactions. Overall, the project aims to leverage technology to uplift the agricultural community, fostering growth, sustainability, and improved productivity in the sector.
Index terms
Integrated E-Commerce Portal, Agriculture, Technological solution, User-friendly platform, Seamless transactions, Collaboration, Farmers, Agribusinesses, Suppliers, Inventory management, Order tracking, Payment processing, Agricultural supply chain, Agricultural products, Services, Seeds, Fertilizers, Equipment, Information hub, Best practices, Market trends, Farming techniques, Digital marketplace, Empowerment, Decision-making processes, Efficiency, Sustainability, Stakeholders, Value chain, Transparency, Growth, Productivity.
-

Data Trustworthiness in Mobile Crowd Sensing
Vol. 1 No. 03 (2024)Abstract
The project, "Data Trustworthiness in Mobile Crowd Sensing," aims to address the critical issue of ensuring the reliability and authenticity of data collected through mobile crowd sensing applications. In the rapidly evolving landscape of sensor-equipped smartphones and ubiquitous connectivity, leveraging the collective intelligence of a crowd for data acquisition has become increasingly popular. However, the inherent challenges of ensuring the trustworthiness of data gathered from diverse sources pose significant obstacles.
This project focuses on developing robust mechanisms and algorithms to validate and authenticate data in the context of mobile crowd sensing. The research encompasses the design and implementation of stringent data collection protocols, authentication measures, and quality control mechanisms to filter out inaccurate or fraudulent data points. The goal is to enhance the overall reliability of information collected from various contributors.
In addition to technical aspects, the project emphasizes the importance of creating a transparent and collaborative environment. Privacy-preserving techniques and clear communication regarding data usage policies are integral components to foster trust among contributors. By addressing these aspects, the project aims to establish a framework that ensures the anonymity and privacy of participants while building a foundation of trust in the mobile crowd sensing ecosystem.
Ultimately, the outcomes of this project are expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of reliable data collection practices in mobile crowd sensing applications, fostering innovation in areas such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and healthcare.
Index Terms
Mobile Crowd Sensing, Data Trustworthiness, Data Authentication, Data Validation, Reliability, Authenticity, Sensor-equipped Smartphones, Ubiquitous Connectivity, Collective Intelligence, Data Collection Protocols, Quality Control Mechanisms, Fraudulent Data, Privacy-preserving Techniques, Data Usage Policies, Transparency, Collaboration, Privacy, Anonymity, Environmental Monitoring, Urban Planning, Healthcare.
-

Enhancing Image Security through Cryptographic Steganography
Vol. 2 No. 08 (2025)Abstract:
In today's digital age, ensuring the security and confidentiality of image data is paramount, particularly with the proliferation of online communication and storage platforms. This project proposes a hybrid approach for enhancing image security by synergistically integrating encryption and steganography techniques. The combination of these two methods aims to fortify the protection of digital images against unauthorized access and tampering. Encryption ensures the confidentiality of image content by converting it into an unintelligible form using robust cryptographic algorithms. Concurrently, steganography conceals the encrypted data within the image itself, embedding it imperceptibly into the pixels or metadata. The synergy of encryption and steganography not only safeguards the integrity of image data but also adds an additional layer of concealment, making it arduous for adversaries to detect and decipher sensitive information. Through this project, the efficacy of the hybrid approach will be evaluated through experimentation and analysis, with the ultimate goal of providing a comprehensive solution for image security in various applications and contexts.
-

Enhanced Weather Forecasting: Integrating Firefly Optimization with Deep Recurrent Neural Networks
Vol. 2 No. 03 (2025)Abstract
The project "Weather Prediction Using Firefly Optimization and Deep Recurrent Neural Networks (DRNN)" explores the integration of two powerful techniques, Firefly optimization and DRNN, to enhance weather forecasting accuracy. Weather prediction is crucial for various industries and sectors, including agriculture, transportation, and disaster management. However, the inherent complexity and dynamic nature of weather systems pose significant challenges to accurate forecasting. Traditional forecasting methods often struggle to capture intricate temporal patterns and dependencies present in meteorological data.
In this project, the team proposes a novel approach that combines the strengths of Firefly optimization, a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the flashing behavior of fireflies, with DRNN, a type of neural network tailored for sequential data analysis. Firefly optimization is employed to optimize the parameters of the DRNN model, facilitating efficient training and enhancing its predictive capabilities. By leveraging Firefly optimization's ability to effectively explore the solution space and DRNN's capacity to capture temporal dependencies, the integrated approach aims to improve the accuracy of weather predictions.
The project involves the implementation and experimentation of the proposed methodology using real-world weather datasets. Performance evaluations will be conducted to assess the effectiveness of the combined approach in comparison to traditional forecasting methods. The outcomes of this project are expected to contribute to the advancement of weather prediction techniques, offering potential benefits in terms of improved forecasting accuracy and reliability. Additionally, the project provides valuable insights for researchers and practitioners in the field of meteorology and related domains.
Index Terms
Weather Prediction, Firefly Optimization, Deep Recurrent Neural Networks (DRNN), Forecasting Accuracy, Meteorological Data, Traditional Forecasting Methods, Temporal Patterns, Sequential Data Analysis, Solution Space Exploration, Parameter Optimization, Performance Evaluation, Real-World Datasets, Advancements in Weather Prediction, Meteorology Research, Disaster Management
-

ADVANCED AI-DRIVEN SYSTEM FOR VECHICLE CLASSIFICATION AND AUTOMATED NUMBER PLATE RECOGNITION
Vol. 1 No. 1 (2024)ABSTRACT
This paper presents an advanced AI-driven system designed for vehicle classification and automated numberplate recognition (ANPR). Leveraging state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms, the system offers robust performance in diverse environmental conditions. The core components include convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image processing and optical character recognition (OCR) for number plate detection. The proposed solution demonstrates high accuracy and speed, making it suitable for real-time applications in traffic management and law enforcement. This innovative approach not only improves the efficiency and accuracy of vehicle identification but also reduces the need for manual intervention, paving the way for smarter, more autonomous traffic systems.The AI-driven system is built on a scalable architecture that can be easily integrated into existing traffic management infrastructures. This flexibility ensures that the system can be adapted to various urban and rural settings, addressing the unique challenges posed by different environments. The incorporation of machine learning models enables continuous improvement of the system’s performance over time, as it learns from new data and adapts to changing conditions. The paper discusses the technical details of the system, including the data preprocessing, model training, and deployment processes.
INDEX TERMS
Vehicle Classification, Automated Number Plate Recognition, Convolutional Neural Networks, Optical Character Recognition, Machine Learning, Traffic Management, Law Enforcement, Real-Time Processing, Image Processing, Deep Learning.
-

Leveraging AI and Multimedia Analysis for Proactive Suicide Prevention
Vol. 2 No. 06 (2025)Abstract
This project aims to address the critical issue of suicide prevention by leveraging machine learning techniques for early detection of potential suicidal tendencies. Suicide is a global public health concern, and timely identification of individuals at risk can significantly contribute to intervention and support.
The project focuses on the utilization of diverse data sources, such as social media posts, online behavior, and multimedia content, to develop an intelligent algorithm capable of recognizing patterns indicative of suicidal thoughts or intentions. Natural language processing and sentiment analysis techniques are employed to scrutinize textual content for linguistic cues associated with distress. Furthermore, image and video analysis techniques, including facial expression recognition and body language analysis, contribute to a comprehensive approach in identifying visual indicators of self-harm or suicidal ideation.
The research involves the development and training of machine learning models on diverse datasets to ensure robust and accurate detection capabilities. The project emphasizes the ethical considerations surrounding privacy and responsible use of technology, aiming to strike a balance between aiding mental health professionals and respecting individual privacy.
The successful implementation of this project could lead to the creation of a valuable tool for mental health practitioners and support systems, enabling them to intervene proactively and provide timely assistance to individuals at risk of suicide.
Index terms
Suicide prevention, Machine learning techniques, Early detection, Suicidal tendencies, Global public health concern, Timely identification, Intervention and support, Diverse data sources, Social media posts, Online behavior, Multimedia content, Intelligent algorithm, Recognizing patterns, Suicidal thoughts or intentions, Natural language processing, Sentiment analysis, Linguistic cues, Distress detection, Image analysis techniques, Video analysis techniques, Facial expression recognition, Body language analysis, Visual indicators, Self-harm, Suicidal ideation, Machine learning models, Ethical considerations, Privacy concerns, Responsible technology use, Mental health professionals, Support systems, Proactive intervention, Timely assistance.
-

Building a Network Traffic Analyzer for Security Monitoring
Vol. 1 No. 05 (2024)Abstract
The project titled "Building a Network Traffic Analyzer for Security Monitoring" addresses the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures in today's interconnected digital landscape. With the ever-increasing threat of cyber-attacks, organizations require advanced tools to monitor and safeguard their network infrastructure. This project aims to develop a sophisticated network traffic analyzer that provides real-time monitoring and analysis of network activities for enhanced security.
The proposed system focuses on capturing and analyzing network traffic using state-of-the-art technologies, ensuring a comprehensive view of the data traversing the network. The project incorporates machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and suspicious patterns, enabling the identification of potential security threats.
The user interface is designed with a user-friendly dashboard, featuring intuitive visualizations and tools to empower security professionals in quickly interpreting the data. The system includes alerting mechanisms to promptly notify administrators of any detected anomalies, enabling swift response to potential security incidents.
This project not only emphasizes the technical aspects of building a powerful network traffic analyzer but also addresses the importance of cybersecurity in safeguarding sensitive information. The implementation of this system contributes to the enhancement of network security protocols, providing organizations with a valuable tool to proactively monitor and mitigate potential risks.
Keywords
Network Traffic Analyzer, Security Monitoring, Cybersecurity, Real-time Monitoring, Network Activities, Machine Learning Algorithms, Anomaly Detection, User Interface, Dashboard Visualization, Alerting Mechanisms, Network Security Protocols, Risk Mitigation, Digital Landscape, Data Analysis, Threat Detection
-

Zero-Shot Multilingual Sentiment Analysis Using Transformer-Based Models
Vol. 2 No. 02 (2025)Abstract
This project aims to explore the feasibility and effectiveness of zero-shot multilingual sentiment analysis using transformer-based models. Traditional sentiment analysis techniques often rely on language-specific models trained on large corpora of labeled data, making them impractical for analyzing sentiments across multiple languages. In contrast, transformer models, such as BERT and GPT, have shown promising results in natural language understanding tasks by leveraging large-scale pre-training and fine-tuning on specific tasks. This project proposes to extend the capabilities of transformer models to perform sentiment analysis across various languages without requiring language-specific training data. The project will involve pre-training a transformer model on multilingual text data and fine-tuning it on sentiment analysis tasks using transfer learning techniques. The effectiveness of the proposed approach will be evaluated on standard benchmark datasets in multiple languages, measuring the accuracy and robustness of sentiment predictions. The outcomes of this project have the potential to significantly enhance the applicability of sentiment analysis tools in multilingual settings, catering to diverse linguistic communities and enabling broader cross-cultural sentiment analysis applications.
Index terms
Zero-shot sentiment analysis, Multilingual sentiment analysis ,Transformer-based models ,BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), Natural language understanding, Transfer learning, Pre-training, Fine-tuning, Sentiment analysis tasks, Benchmark datasets, Accuracy measurement, Robustness assessment, Cross-cultural sentiment analysis, Linguistic diversity, Applicability enhancement, Language-specific models, Large corpora, Feasibility study, Effectiveness evaluation.
-
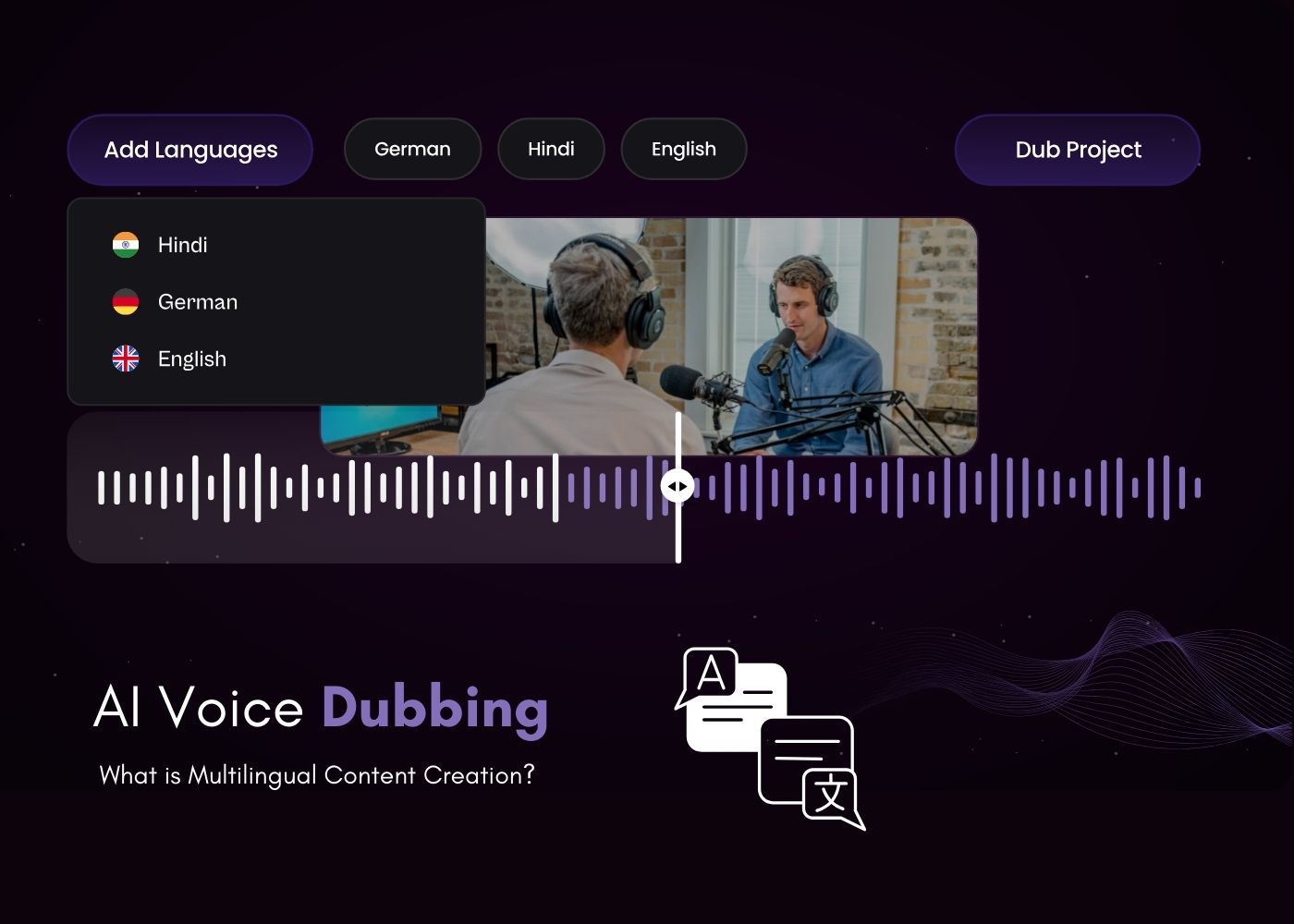
AI-Powered Automated Video Dubbing System with Multi-Language Support and Lip Synchronization
Vol. 3 No. 1 (2026)The exponential expansion of digital multimedia across international platforms necessitates efficient multilingual dubbing solutions. Conventional dubbing methodologies prove resource-intensive and economically prohibitive for widespread content localization. This research introduces an intelligent automated dubbing framework integrating advanced neural architectures for speech processing, translation, and synthesis. The system employs Whisper for acoustic modeling, NLLB-200 for cross-lingual translation, XTTS v2 for voice cloning, and Wav2Lip GAN for visual synchronization. A novel segment-based processing approach ensures temporal precision between synthesized audio and source video. Experimental validation demonstrates superior naturalness and synchronization accuracy compared to existing methodologies. The framework addresses critical applications in educational technology, digital entertainment, corporate communication, and accessibility enhancement.
-

SafeCam: Real-Time Accident Detection & Alerts
Vol. 2 No. 05 (2025)Abstract
The project "Safe Cam: Real-Time Accident Alerts" aspires to revolutionize road safety through the development of an innovative technological solution. By harnessing advanced camera and sensor systems, the project's primary aim is to detect accidents as they occur in real-time, providing users with immediate and accurate alerts through a user-friendly application interface. Through this proactive approach, drivers gain the ability to make informed decisions regarding their routes, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents and navigating around potential traffic congestion more efficiently.
At its core, the significance of the "Safe Cam" project lies in its potential to enhance the driving experience by prioritizing safety through technology. By empowering drivers with timely information about accidents, the project not only fosters a culture of safer driving habits but also emphasizes the pivotal role of technology in addressing critical road safety concerns. Through the seamless integration of real-time accident detection and user notification systems, "Safe Cam" aims to contribute to a safer and more efficient driving environment, underscoring the importance of leveraging technological advancements to mitigate road hazards effectively.
Index terms
Safe Cam, Real-time accident alerts, Road safety, Technological solution, Advanced camera systems, Sensor systems, Accident detection, User-friendly application interface, Proactive approach, Informed decision-making, Traffic congestion, driving experience, Safer driving habits, Technology integration, User notification systems, Driving environment, Technological advancements, Road hazards, Safety prioritization.
-
Enhancing Network Security through Intrusion Detection Systems
Vol. 1 No. 03 (2024)Abstract
The project titled "Enhancing Network Security through Intrusion Detection Systems" aims to explore and implement advanced techniques to strengthen the security posture of computer networks. In today's digital landscape, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, the role of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) becomes crucial in detecting and mitigating potential security breaches.
The project focuses on the comprehensive understanding and deployment of both signature-based and anomaly-based IDS approaches. It delves into the development of a robust system capable of monitoring network traffic, identifying known attack patterns, and detecting deviations from normal behavior. By combining these methods, the project aims to provide a more effective defense against a wide range of cyber threats.
Furthermore, the project incorporates the integration of machine learning algorithms within the IDS framework. This addition allows the system to learn and adapt to emerging threats, thereby improving its ability to detect previously unknown and sophisticated attacks. The implementation of machine learning contributes to a dynamic and intelligent intrusion detection mechanism, reducing false positives and enhancing overall accuracy.
The outcomes of this project will not only contribute to the academic understanding of network security but will also provide practical insights into implementing advanced intrusion detection techniques. Ultimately, the project seeks to empower organizations with a more resilient defense against cyber threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their networked systems.
-

Data Trustworthiness in mobile Crowd Sensing With ML
Vol. 2 No. 08 (2025)Abstract
The project, "Data Trustworthiness in Mobile Crowd Sensing ML," aims to address the critical issue of ensuring the reliability and authenticity of data collected through mobile crowd sensing applications. In the rapidly evolving landscape of sensor-equipped smartphones and ubiquitous connectivity, leveraging the collective intelligence of a crowd for data acquisition has become increasingly popular. However, the inherent challenges of ensuring the trustworthiness of data gathered from diverse sources pose significant obstacles.
This project focuses on developing robust mechanisms and algorithms to validate and authenticate data in the context of mobile crowd sensing. The research encompasses the design and implementation of stringent data collection protocols, authentication measures, and quality control mechanisms to filter out inaccurate or fraudulent data points. The goal is to enhance the overall reliability of information collected from various contributors.
In addition to technical aspects, the project emphasizes the importance of creating a transparent and collaborative environment. Privacy-preserving techniques and clear communication regarding data usage policies are integral components to foster trust among contributors. By addressing these aspects, the project aims to establish a framework that ensures the anonymity and privacy of participants while building a foundation of trust in the mobile crowd sensing ecosystem.
Ultimately, the outcomes of this project are expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of reliable data collection practices in mobile crowd sensing applications, fostering innovation in areas such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and healthcare.
Index Terms
Mobile Crowd Sensing, Data Trustworthiness, Data Authentication, Data Validation, Reliability, Authenticity, Sensor-equipped Smartphones, Ubiquitous Connectivity, Collective Intelligence, Data Collection Protocols, Quality Control Mechanisms, Fraudulent Data, Privacy-preserving Techniques, Data Usage Policies, Transparency, Collaboration, Privacy, Anonymity, Environmental Monitoring, Urban Planning, Healthcare.
-

Digital Campus Tour Realistic 3D Walkthrough with Interactive Features
Vol. 2 No. 03 (2025)Abstract
This project aims to develop a Virtual Campus Walkthrough application utilizing the three.js library, offering an immersive and interactive experience for users to explore a digital representation of a campus environment. The application will allow users to navigate through the virtual campus using keyboard or mouse inputs, providing a simulated experience akin to physically walking through the real campus. Leveraging the capabilities of three.js, the application will render high-quality 3D graphics and textures, ensuring a visually compelling and realistic environment. Users will have the opportunity to interact with various elements within the virtual campus, such as buildings, landmarks, and informational points of interest. The project will focus on creating a user-friendly interface, optimizing performance for smooth navigation, and integrating interactive features to enhance the overall experience. Ultimately, the Virtual Campus Walkthrough aims to provide a valuable tool for prospective students, faculty, and visitors to explore and familiarize themselves with the campus remotely.
Index Terms
Virtual Campus Walkthrough, three.js library, Immersive Experience, Interactive Exploration, Digital Representation, Campus Environment, Navigation Controls, 3D Graphics, Textures Rendering, Realistic Environment, User Interaction, User-Friendly Interface, Performance Optimization, Interactive Features, Prospective Students, Faculty, Visitors, Remote Exploration.
-

PERSONALIZED SKINCARE PRODUCTS RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM USING ML AND DL
Vol. 1 No. 1 (2024)Abstract The personalized skincare product recommendation system leverages machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) techniques to provide tailored product suggestions based on individual skin profiles. The system utilizes a combination of user input, skin condition analysis, and product data to deliver recommendations that address specific skincare needs. By integrating advanced ML algorithms and DL models, the system aims to enhance user experience, improve skincare outcomes, and drive engagement with personalized recommendations. This paper details the design, implementation, and evaluation of the system, demonstrating its efficacy in delivering accurate and relevant skincare product recommendations.Index TermsPersonalized Skincare, Product Recommendation, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Skin Analysis, Recommendation Systems, User Profiling, AI in Beauty, Skincare Data, PredictiveModeling, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recommender Systems, User Experience.1. IntroductionPersonalized skincare is an emerging field where individual skin characteristics and needs drive the selection of appropriate products. Traditional skincare product recommendations are often generic, lacking personalization and not accounting for unique skin conditions. Advances in machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) offer a transformative approach to building sophisticated recommendation systems that can analyze user data, such as skin type, concerns, and preferences, to suggest tailored skincare solutions.Machine learning algorithms enable the processing of large datasets, extracting patterns, and making predictions based on historical user data and product efficacy. Deep learning models, particularly those using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs), enhance the system's capability to understand complex relationships between user profiles and product features. This integration allows for a more precise and individualized approach to skincare recommendations.The need for personalized skincare solutions is driven by increasing consumer demand for products that address specific skin concerns such as acne, aging, or sensitivity. Traditional approaches to skincare often rely on broad categorizations that may not fully address individual needs. By incorporating ML and DL into the recommendation system, the proposed solution aims to bridge this gap, providing users with personalized product suggestions that are more likely to meet their specific requirements.This paper explores the development of a personalized skincare recommendation system, detailing the methodologies employed, thedesign of the recommendation algorithms, and the evaluation of system performance. The integration of ML and DL techniques into the recommendation process offers a novel approach to enhancing user satisfaction and optimizing skincare outcomes. -

Block chain-Powered Digital Certificate Verification System
Vol. 2 No. 07 (2025)Abstract
This project aims to explore the application of blockchain technology in enhancing the verification and validation processes of digital certificates. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the need for secure and reliable methods of validating credentials becomes paramount. Traditional methods of certificate verification often face challenges related to security and trust.
The project focuses on leveraging the decentralized and tamper-resistant nature of blockchain to establish a robust framework for digital certificate verification. Through the implementation of smart contracts and cryptographic principles, the proposed system ensures the integrity and authenticity of digital certificates. The blockchain network acts as a distributed ledger, recording and validating certificate transactions across multiple nodes.
Key objectives of the project include designing a user-friendly interface for certificate submission and verification, implementing secure cryptographic techniques for digital signatures, and integrating smart contracts to automate the validation process. The project also explores the potential scalability and efficiency benefits of blockchain technology in handling large-scale certificate verification scenarios.
Through this endeavor, this project aims to contribute to the advancement of secure credential verification systems, addressing the challenges associated with traditional methods. The project aligns with the broader goals of enhancing digital trust and security, offering a practical and innovative solution for validating digital certificates using cutting-edge blockchain technology.
Index Terms
Blockchain technology, Digital certificates, Verification processes, Validation processes, Decentralization, Tamper-resistance, Smart contracts, Cryptographic principles, Distributed ledger, User-friendly interface, Cryptographic techniques, Digital signatures, Scalability, Efficiency, Credential verification systems, Digital trust, Security, Innovation.
-

Development of an LSTM-Based System for Real-Time Toxic Comment Classification in Online Platforms
Vol. 1 No. 05 (2024)Abstract
The project aims to develop an efficient and accurate system for classifying toxic comments in online platforms using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. With the exponential growth of online content, ensuring a safe and respectful environment for users is of paramount importance. Toxic comments, characterized by offensive, abusive, or harmful language, pose a significant challenge for content moderation.
This project employs LSTM, a type of recurrent neural network, known for its ability to capture sequential dependencies in data. The LSTM model will be trained on a labeled dataset comprising both toxic and non-toxic comments. During training, the model learns to recognize patterns and contextual cues associated with toxic language, enabling it to make predictions on unseen comments.
The implementation involves preprocessing textual data, constructing an LSTM architecture, and fine-tuning the model to achieve optimal performance. The trained LSTM model will be integrated into an interactive platform, providing real-time classification of comments. The project will also explore techniques for model evaluation, addressing challenges such as false positives and false negatives.
The successful implementation of this project can significantly contribute to enhancing online content moderation, fostering healthier digital communication spaces, and mitigating the impact of toxic behavior. Additionally, the project offers valuable insights into the application of deep learning techniques, specifically LSTM, in addressing real-world social challenges related to online content.
Index Terms
Toxic comments, Online platforms, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, Content moderation, Recurrent neural network, Sequential dependencies, Labeled dataset, Textual data preprocessing, Model fine-tuning, Real-time classification, Model evaluation, False positives, False negatives, Digital communication spaces, Deep learning techniques.
-

Carbon-Conscious AI: Reducing the Environmental Impact of Deep Learning
Vol. 2 No. 10 (2025)Deep learning has achieved remarkable progress in recent years, powering applications
ranging from natural language processing to computer vision and autonomous systems.
However, this rapid growth has come with a significant environmental cost. Training large-
scale models requires vast computational resources, which in turn lead to high energy
consumption and substantial carbon emissions. The environmental footprint of AI research is
increasingly recognized as a critical challenge, raising concerns about sustainability and
ethical deployment. This paper examines the issue of carbon-conscious AI, focusing on
strategies to reduce the environmental impact of deep learning. We provide a literature
review of existing work on energy-efficient AI, discuss techniques such as model compression,
neural architecture search, and efficient hardware utilization, and propose a framework for
integrating carbon-awareness into AI development pipelines. Simulation-based evaluations
show that adopting energy-aware training and inference strategies can reduce carbon
emissions by up to 40% without compromising model accuracy. We conclude with future
directions for building sustainable AI ecosystems through interdisciplinary collaboration
among researchers, industry, and policymakers.




