
Archives - Page 4
-

SafeCam: Real-Time Accident Detection & Alerts
Vol. 2 No. 05 (2025)Abstract
The project "Safe Cam: Real-Time Accident Alerts" aspires to revolutionize road safety through the development of an innovative technological solution. By harnessing advanced camera and sensor systems, the project's primary aim is to detect accidents as they occur in real-time, providing users with immediate and accurate alerts through a user-friendly application interface. Through this proactive approach, drivers gain the ability to make informed decisions regarding their routes, ultimately reducing the risk of accidents and navigating around potential traffic congestion more efficiently.
At its core, the significance of the "Safe Cam" project lies in its potential to enhance the driving experience by prioritizing safety through technology. By empowering drivers with timely information about accidents, the project not only fosters a culture of safer driving habits but also emphasizes the pivotal role of technology in addressing critical road safety concerns. Through the seamless integration of real-time accident detection and user notification systems, "Safe Cam" aims to contribute to a safer and more efficient driving environment, underscoring the importance of leveraging technological advancements to mitigate road hazards effectively.
Index terms
Safe Cam, Real-time accident alerts, Road safety, Technological solution, Advanced camera systems, Sensor systems, Accident detection, User-friendly application interface, Proactive approach, Informed decision-making, Traffic congestion, driving experience, Safer driving habits, Technology integration, User notification systems, Driving environment, Technological advancements, Road hazards, Safety prioritization.
-
Enhancing Network Security through Intrusion Detection Systems
Vol. 1 No. 03 (2024)Abstract
The project titled "Enhancing Network Security through Intrusion Detection Systems" aims to explore and implement advanced techniques to strengthen the security posture of computer networks. In today's digital landscape, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, the role of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) becomes crucial in detecting and mitigating potential security breaches.
The project focuses on the comprehensive understanding and deployment of both signature-based and anomaly-based IDS approaches. It delves into the development of a robust system capable of monitoring network traffic, identifying known attack patterns, and detecting deviations from normal behavior. By combining these methods, the project aims to provide a more effective defense against a wide range of cyber threats.
Furthermore, the project incorporates the integration of machine learning algorithms within the IDS framework. This addition allows the system to learn and adapt to emerging threats, thereby improving its ability to detect previously unknown and sophisticated attacks. The implementation of machine learning contributes to a dynamic and intelligent intrusion detection mechanism, reducing false positives and enhancing overall accuracy.
The outcomes of this project will not only contribute to the academic understanding of network security but will also provide practical insights into implementing advanced intrusion detection techniques. Ultimately, the project seeks to empower organizations with a more resilient defense against cyber threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their networked systems.
-

Data Trustworthiness in mobile Crowd Sensing With ML
Vol. 2 No. 08 (2025)Abstract
The project, "Data Trustworthiness in Mobile Crowd Sensing ML," aims to address the critical issue of ensuring the reliability and authenticity of data collected through mobile crowd sensing applications. In the rapidly evolving landscape of sensor-equipped smartphones and ubiquitous connectivity, leveraging the collective intelligence of a crowd for data acquisition has become increasingly popular. However, the inherent challenges of ensuring the trustworthiness of data gathered from diverse sources pose significant obstacles.
This project focuses on developing robust mechanisms and algorithms to validate and authenticate data in the context of mobile crowd sensing. The research encompasses the design and implementation of stringent data collection protocols, authentication measures, and quality control mechanisms to filter out inaccurate or fraudulent data points. The goal is to enhance the overall reliability of information collected from various contributors.
In addition to technical aspects, the project emphasizes the importance of creating a transparent and collaborative environment. Privacy-preserving techniques and clear communication regarding data usage policies are integral components to foster trust among contributors. By addressing these aspects, the project aims to establish a framework that ensures the anonymity and privacy of participants while building a foundation of trust in the mobile crowd sensing ecosystem.
Ultimately, the outcomes of this project are expected to contribute significantly to the advancement of reliable data collection practices in mobile crowd sensing applications, fostering innovation in areas such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, and healthcare.
Index Terms
Mobile Crowd Sensing, Data Trustworthiness, Data Authentication, Data Validation, Reliability, Authenticity, Sensor-equipped Smartphones, Ubiquitous Connectivity, Collective Intelligence, Data Collection Protocols, Quality Control Mechanisms, Fraudulent Data, Privacy-preserving Techniques, Data Usage Policies, Transparency, Collaboration, Privacy, Anonymity, Environmental Monitoring, Urban Planning, Healthcare.
-

Zero-Shot Multilingual Sentiment Analysis Using Transformer-Based Models
Vol. 2 No. 02 (2025)Abstract
This project aims to explore the feasibility and effectiveness of zero-shot multilingual sentiment analysis using transformer-based models. Traditional sentiment analysis techniques often rely on language-specific models trained on large corpora of labeled data, making them impractical for analyzing sentiments across multiple languages. In contrast, transformer models, such as BERT and GPT, have shown promising results in natural language understanding tasks by leveraging large-scale pre-training and fine-tuning on specific tasks. This project proposes to extend the capabilities of transformer models to perform sentiment analysis across various languages without requiring language-specific training data. The project will involve pre-training a transformer model on multilingual text data and fine-tuning it on sentiment analysis tasks using transfer learning techniques. The effectiveness of the proposed approach will be evaluated on standard benchmark datasets in multiple languages, measuring the accuracy and robustness of sentiment predictions. The outcomes of this project have the potential to significantly enhance the applicability of sentiment analysis tools in multilingual settings, catering to diverse linguistic communities and enabling broader cross-cultural sentiment analysis applications.
Index terms
Zero-shot sentiment analysis, Multilingual sentiment analysis ,Transformer-based models ,BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), Natural language understanding, Transfer learning, Pre-training, Fine-tuning, Sentiment analysis tasks, Benchmark datasets, Accuracy measurement, Robustness assessment, Cross-cultural sentiment analysis, Linguistic diversity, Applicability enhancement, Language-specific models, Large corpora, Feasibility study, Effectiveness evaluation.
-
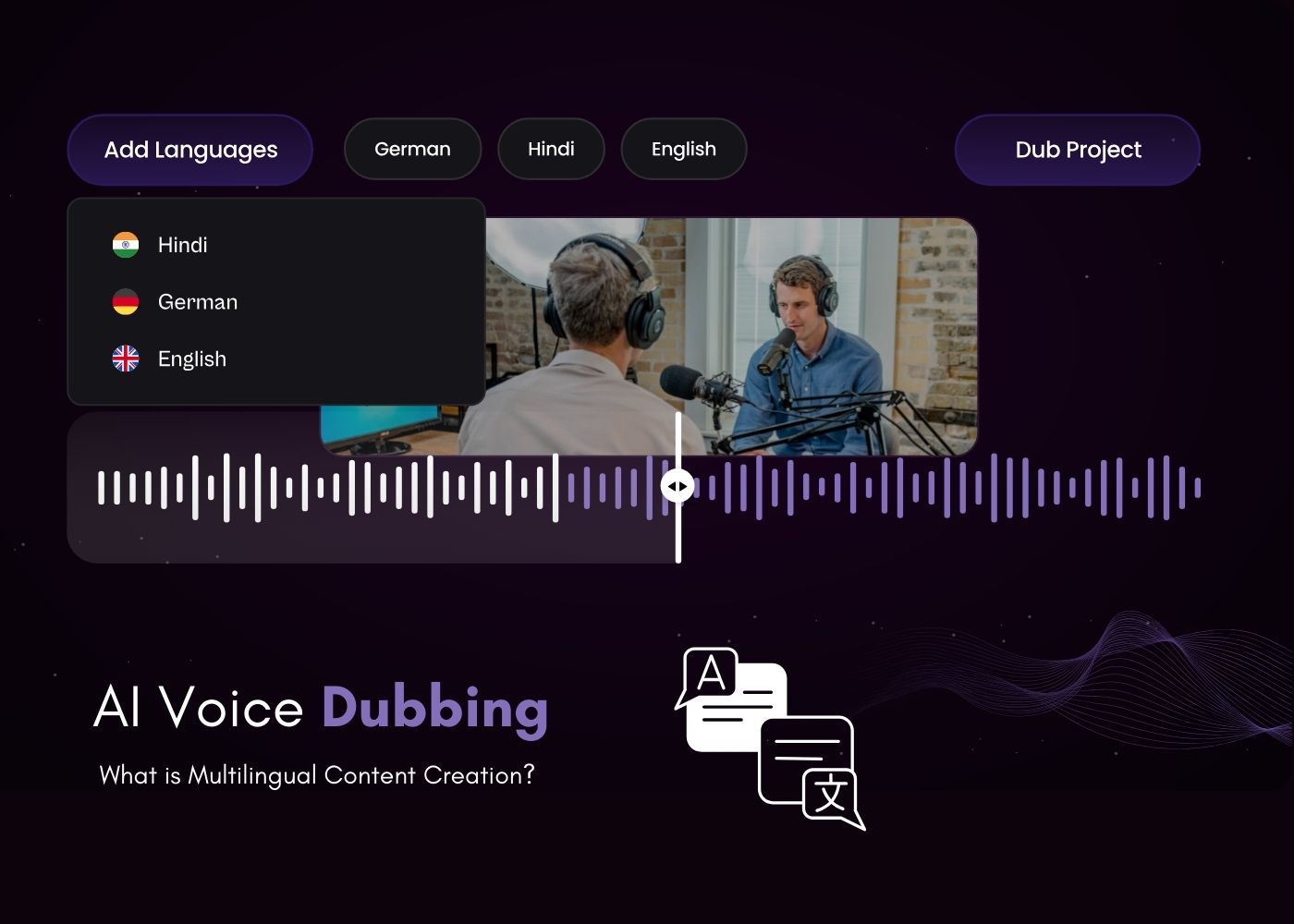
AI-Powered Automated Video Dubbing System with Multi-Language Support and Lip Synchronization
Vol. 3 No. 1 (2026)The exponential expansion of digital multimedia across international platforms necessitates efficient multilingual dubbing solutions. Conventional dubbing methodologies prove resource-intensive and economically prohibitive for widespread content localization. This research introduces an intelligent automated dubbing framework integrating advanced neural architectures for speech processing, translation, and synthesis. The system employs Whisper for acoustic modeling, NLLB-200 for cross-lingual translation, XTTS v2 for voice cloning, and Wav2Lip GAN for visual synchronization. A novel segment-based processing approach ensures temporal precision between synthesized audio and source video. Experimental validation demonstrates superior naturalness and synchronization accuracy compared to existing methodologies. The framework addresses critical applications in educational technology, digital entertainment, corporate communication, and accessibility enhancement.




